Intro: Why automation matters now
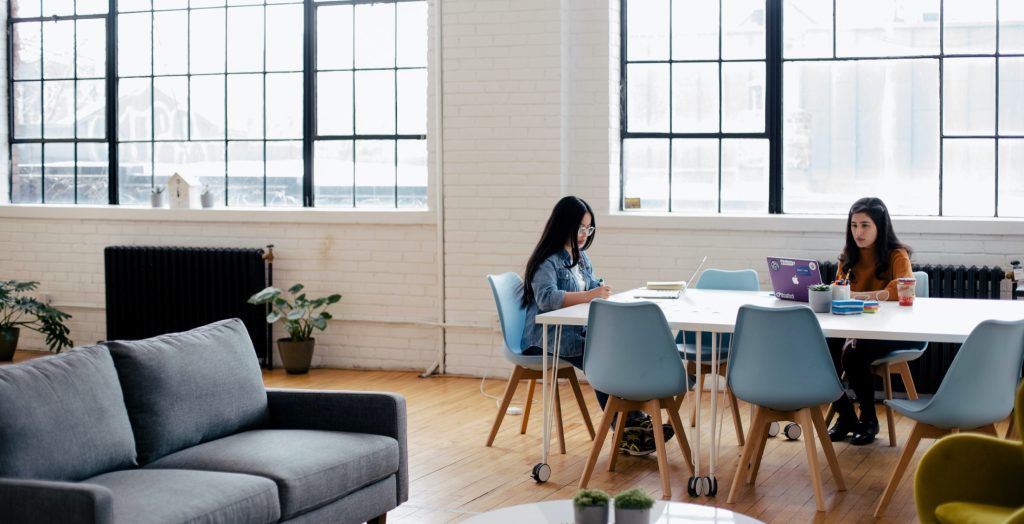
AI customer service automation has moved from novelty pilots to production-critical systems in many companies. For consumers, that means faster answers, fewer transfers, and 24/7 support. For businesses, it promises lower handle times, consistent SLA compliance, and new channels for product feedback. This article explains how to design, build, and operate practical automation systems that combine conversational AI, orchestration, and backend integration — without drowning in complexity or vendor lock-in.
For the beginner: what this actually looks like
Imagine a mid-sized online retailer. A customer wants to change a shipping address. Today they might call, wait on hold, and get transferred. With AI customer service automation, the customer types into chat, the system understands intent, verifies identity, updates the order status, and confirms the change — all in minutes. If the system can’t handle a subtle exception, it escalates to a human with context so the agent doesn’t need to ask repetitive questions.
Analogy: think of the system as an experienced front-desk assistant who handles routine tasks and only rings the manager for rarer problems. The assistant uses checklists, looks up records, and follows routing rules — that’s automation plus AI wrapped into a workflow.
Platform types and trade-offs
There are three common platform patterns for AI-driven customer service automation:
- Managed SaaS orchestration: Turnkey tools (Zendesk with AI add-ons, Salesforce Einstein, or specialized offerings) provide fast time-to-value. Trade-off: limited customization and potential data residency or cost concerns.
- Self-hosted stacks: Open-source components such as Rasa for NLU, Temporal or Apache Airflow for orchestration, and your own model serving layer. Trade-off: more operational burden but full control and potentially lower long-term cost.
- Hybrid architectures: Core orchestration and integrations self-hosted while using managed model inference (Hugging Face Inference, managed LLMs) or managed observability. These balance agility and operational cost.
Architectural patterns: from intent to action
Designing a resilient automation system requires separating concerns into discrete layers:
- Input and understanding: NLU, intent classification, entity extraction. This can be provided by models fine-tuned on domain data or by retrieval-augmented generation for richer context.
- State and memory: Conversation state, session context, and long-term customer memory. Some systems store persistent attributes like purchase history; thoughtful retention policies and governance are critical here.
- Orchestration and decisioning: The brain that sequences tasks. It invokes APIs, triggers backend jobs, hands off to humans, and logs outcomes. Tools like Temporal or Durable Functions offer durable task orchestration patterns suitable for multi-step transactions.
- Integration layer: Canonical APIs and adapters for CRM, billing, fulfillment, and authentication systems. This layer enforces contracts and abstracts backend differences.
- Model serving and inference: Where speech-to-text, intent models, and response generation run. Serving choices impact latency, cost, and privacy.
Integration and API design
API design is central. When building automation you benefit from a few consistent practices:
- Define small, versioned endpoints for business actions (confirm_order, change_address) rather than exposing low-level DB operations.
- Prefer idempotent operations to support retries and durable workflows.
- Support both synchronous and asynchronous patterns: webhooks for event-driven updates and REST/gRPC for immediate operations. This is the area where AI in API development becomes operational: APIs should provide structured context to models and accept structured outputs in return.
- Standardize telemetry fields (request_id, session_id, intent_score) for tracing across the stack.
Model serving, costs, and memory-efficient choices
Serving models close to production needs is a cost-performance decision. High-throughput conversational systems often use a mix of lightweight classifiers for intent (fast, cheap) and larger generative models for complex responses (slower, expensive). Here, AI memory-efficient models become a key consideration.
Strategies to manage inference costs and footprint:
- Distillation and small architectures: Use distilled or compact models for routine intent detection and classification. Distilled models maintain accuracy while reducing parameter counts.
- Quantization and pruning: Techniques like 8-bit quantization or structured pruning reduce memory usage and improve inference throughput, especially on commodity GPUs and CPUs.
- Routing to specialized models: Implement a lightweight router that sends complex queries to larger models and simple queries to small models to optimize latency and cost.
- Edge and hybrid inference: For privacy-sensitive or low-latency scenarios, perform inference on-device or on-premises using optimized, memory-efficient models.
Popular projects and patterns that help here include Hugging Face model hubs for smaller variants, QLoRA techniques for fine-tuning, and FlashAttention for throughput gains. Choosing the right mix impacts both user experience and operational cost.
Deployment and scaling considerations
Scaling automation systems is about more than adding CPU or GPU. Consider:
- Autoscaling by route: Scale inference pools based on predicted traffic per channel (chat, voice, email). Different channels have different SLOs.
- Backpressure and graceful degradation: When systems are saturated, have fallbacks: use smaller models, offer queued responses, or escalate to human agents with best-effort context transfer.
- Capacity planning: Measure peak concurrent conversations, average tokens per turn, and downstream dependency latencies. These metrics inform GPU and worker pool sizing.
- Latency budgets: For conversational UX, keep end-to-end latency under target thresholds (e.g.,
Observability, testing, and continuous improvement
Operational visibility must cover three planes:

- Infrastructure metrics: CPU, GPU utilization, queue lengths, autoscaler actions.
- Application traces: Distributed tracing tying user session to orchestration steps and backend calls.
- Model signals: Confidence scores, hallucination rates, prompt/context drift, and distributional shifts in user language.
Run canary releases for new models or orchestration changes. Capture labeled failure cases and use them both to retrain models and to tune decisioning rules. Humans-in-the-loop workflows and audit trails are essential for safe improvements.
Security, privacy, and governance
AI in customer automation touches sensitive data. Best practices include:
- Data minimization and retention policies: store only what’s necessary and purge according to policy.
- End-to-end encryption for PII in transit and at rest; tokenization or hashing for identifiers sent to third-party models.
- Access control and RBAC on orchestration flows so that only authorized services or agents can perform state-changing actions.
- Audit logs that record decisions made by models and the human overrides applied, supporting regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, PCI where relevant).
Business metrics, ROI, and real case examples
Track business-focused metrics to justify investment:
- Average handle time (AHT) reduction for automated cases.
- Containment rate: fraction of contacts fully resolved without human escalation.
- Customer satisfaction (CSAT) and automation NPS correlations.
- Cost per contact and total cost of ownership including model licensing and inference costs.
Case in point: a financial services firm reduced AHT by 40% by combining intent classification with a durable workflow engine that handled identity verification, payment changes, and regulatory logging. They used a mix of distilled models for front-line classification and a larger model for drafting responses in complex cases, saving costs while preserving quality.
Vendor comparison and open-source ecosystem
Choose based on priorities:
- Speed to deploy: Managed vendors excel here but review data residency and export controls.
- Control and customization: Open-source stacks like Rasa, Botpress, and orchestration tools like Temporal give flexibility but require ops bandwidth.
- Model ecosystem: Hugging Face, OpenAI, Anthropic and in-house models all offer different trade-offs on cost, privacy, and capability. Evaluate how they handle updates, fine-tuning, and latency.
Recent industry activity — new model releases and improvements in quantization techniques — make it practical to run capable models on less expensive infrastructure, improving ROI for self-hosted options.
Implementation playbook (step-by-step in prose)
Start small and iterate:
- Identify 1–3 high-volume, low-risk use cases (billing queries, basic returns) and map the happy path and exceptions.
- Prototype an NLU+workflow for those paths using a modular stack so components can be swapped out later.
- Define API contracts for backend actions and set up an orchestration layer that persists state and supports retries.
- Run shadow mode to compare AI decisions with human decisions and gather labeled outcomes for retraining.
- Introduce fallbacks, escalation rules, and thresholds for automated decisions to ensure safety.
- Measure business KPIs and expand to additional flows after validating ROI.
Common failure modes and mitigations
- Model drift: Regularly monitor input distributions and set retraining cadences.
- Broken integrations: Use contract tests and circuit breakers to avoid cascading failures.
- Overconfidence: Use calibrated confidence thresholds and require human sign-off for high-impact actions.
- Latency spikes: Implement graceful degradation to smaller models or canned responses.
Standards, policy, and the future
Regulatory scrutiny is increasing for automated decisioning in customer service. Expect expanding requirements for explainability, opt-out mechanisms, and clear labeling of AI interactions. Interoperability standards for conversational context and session transfer are emerging, as are best practices for privacy-preserving model fine-tuning.
Longer-term, look for more modular AI operating systems — orchestration layers that can plug in different models, memory stores, and human workflows — making it easier to evolve systems without large rip-and-replace projects.
Final Thoughts
Building practical AI customer service automation is a multidisciplinary effort. Success comes from pairing good models with robust orchestration, careful API design, clear governance, and observability. By starting with focused use cases, choosing the right mix of managed and self-hosted components, and prioritizing memory-efficient models and solid API contracts, teams can deliver measurable ROI while keeping risk manageable. The landscape will continue to shift as models get cheaper and policy questions clarify, but the fundamental engineering patterns — modular services, durable workflows, and transparent telemetry — will remain central to systems that scale.